Historica
“A generation which ignores history has no past and no future.”
Robert Heinlein, American author (1907-1988)
Was the treaty of Versailles fair?
What was the treaty of versailles?
The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, concluded World War I and imposed harsh penalties on Germany. This treaty has been a subject of intense debate, with historians and scholars grappling with its fairness and long-term consequences.
It addressed several key areas:
Military:
-
Demilitarization: Germany's armed forces were severely limited. The army was reduced to 100,000 men, conscription was abolished, and the navy and air force were significantly curtailed.
-
Rhineland Demilitarization: A demilitarized zone was established along the Rhine River, forbidding German military presence.
-
Conscription was banned.
-
Germany was not allowed an air force, tanks, armored vehicles and U boats.
Economic:
-
Reparations: Germany was forced to pay substantial reparations of 132 billion gold marks to the Allied powers for the damages caused by the war. The initial amount was astronomical and proved to be a crippling burden on the German economy.
-
Loss of Industrial Resources: Germany lost significant industrial resources, including valuable coal mines in the Saar region and iron ore deposits in Alsace-Lorraine. This severely hampered its industrial production and economic growth.
-
Trade Restrictions: The treaty imposed restrictions on German trade, hindering its ability to compete in international markets and recover economically.
Territorial:
-
Loss of Colonies: Germany's overseas colonies were seized by the Allied powers.
-
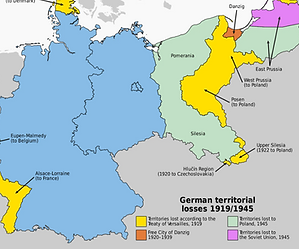
Border Adjustments: Germany's borders were redrawn, with territories ceded to neighboring countries such as France, Poland, and Belgium.
-
Germany lost Alsace Lorraine to France, Saar land was given to the LON.
-
Anschluss with Austria was banned
Blame:
-
War Guilt Clause (Article 231): This controversial clause placed sole responsibility for the war on Germany. This deeply humiliated the German people and fueled resentment towards the Allied powers.


What were the motives and aims of the Big Three at Versailles?

The Paris Peace Conference, where the treaty was negotiated, saw a clash of interests among the "Big Three" leaders:
-
Woodrow Wilson (US): Advocated for his Fourteen Points, emphasizing self-determination, the League of Nations, and a lenient approach towards Germany.
-
Georges Clemenceau (France): Sought to weaken Germany to prevent future aggression, prioritizing French security and demanding heavy reparations.
-
David Lloyd George (UK): Sought a balance between punishing Germany and ensuring European stability, while also considering Britain's economic interests.
PPQs on Woodraw Wilson.
4 Marker on what Wilson wanted to acheive at the conference
-
‘He hoped there would be a fair/just peace.’
-
‘He did not want Germany treated too harshly.’
-
‘He hoped that his Fourteen Points would be accepted.’
-
‘He wanted self-determination for people in Europe.’
-
‘He wanted disarmament.’
-
‘He wanted a settlement that would preserve peace in the future.’
-
‘He hoped that a League of Nations would be set up.’
-
‘He wanted to ban secret treaties.’
-
‘He wanted reparations.’
4 marker on the purpose of Wilsons's 14 points:
-
‘He wanted to build a better world.’
-
‘He wanted countries to live in peace.’
-
‘He wanted to make sure that Germany was not punished too harshly.’
-
‘He believed in self-determination for nations and wanted to achieve this.’
-
‘His purpose was to influence the direction of the peace negotiations at Versailles.’
-
‘He wanted a fair peace settlement.’
-
‘He wanted countries to co-operate with each other in the future.’
6 marker on why Wilson's self determination was important.
-
‘Wilson’s views on self-determination were important because they were unpopular with the French and British. Self-determination meant that different peoples should have the right to rule over themselves. Both France and Britain ruled over large empires. If Wilson’s plans were adopted this would threaten their control over their empires.’
6 marker on why wilson wanted the league of nations
-
‘Wilson thought that a ‘league of nations’ would help to ensure world peace in the future. By representatives from all nations meeting regularly, he believed that problems could be discussed and solutions found to disputes without the need for nations to resort to war.’



6 marker on why self determination failed.
-
‘Wilson’s views were threatening to the British and French governments as both ruled millions of people in their Empires.’
-
‘It was impractical. It would be very difficult to give the peoples of eastern Europe the chance to rule themselves because they were scattered across many countries. Some people were bound to end up being ruled by other nationalities with different customs.’
10 marker ‘Wilson gained what he wanted in the peace negotiations.’ How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer.
Reasons for
-
‘Wilson was pleased that he had successfully persuaded his partners to accept that the Covenant of the League of Nations should be included in all the peace treaties. This would help to make sure that there was a League of Nations. This was one of his main aims because he felt that this would help prevent future wars.’
Reasons against
-
Wilson did not really get what he wanted. War guilt and reparations were not what Wilson had wanted because he did not want Germany to be punished too harshly. Nor did he get everything he wanted over self-determination, especially with Austria. He wanted people to be able to decide who would govern them and this was not applied in Austria which was denied the right to join with Germany.’
10 marker ‘President Wilson was bitterly disappointed by the outcome of the peace negotiations at Versailles.’ How far do you
agree with this statement? Explain your answer.
Reasons for
-
‘I think that Wilson would have been disappointed. He had gone into the negotiations with his 14 Points which he hoped would form the basis of the treaty. However, he was up against Britain and France, both of which had suffered badly during the war. They were not as keen on his points. One of the points was self-determination. This was only partly achieved. Britain and France took Germany’s colonies, which was against self-determination. He also failed to gain other points such as every country reducing armaments and freedom of the seas. The problem was that Wilson, the idealist, was up against pragmatic politicians such as Lloyd George and Clemenceau who both wanted to get the best they could for their own countries.’
Reasons against
-
‘Wilson was generally pleased with what had been achieved. He had managed to get some of the worst of Clemenceau’s demands to be rejected. For example, the Rhineland was not going to be made into a separate state or given to France. It remained as part of Germany. This allowed Germany to remain as a major economic power and keep trading with the USA.’
PPQs on Clemenceau
4 marker on what did clemenceau want
-
‘He wanted security for France.’
-
‘He wanted to weaken Germany.’
-
‘Germany’s armed forces to be disbanded.’
-
‘Germany to pay reparations for the damage it caused in the war.’
-
‘Alsace-Lorraine to be returned to France.’
-
‘The Rhineland to become an independent state.’
-
‘The Saar basin to go to France.’
-
‘Some German colonies to be handed to France.’
4 marker on Clemenceau's territorial demands
-
‘Alsace-Lorraine had to be returned to France.’
-
‘He wanted some of Germany’s colonies.’
-
‘The Saar Basin was to be given to France.’
-
‘He wanted the Rhineland to be an independent state to give France
-
protection from a German attack.’
6 marker on why Clemenceau wanted a harsh treaty
-
‘Clemenceau wanted a harsh peace because he wanted to make sure that Germany could not invade France again. He wanted to weaken Germany’s armed forces and strengthen France’s borders. Germany had a bigger population than France and the two countries had a common border so Clemenceau was worried that there was always the danger of another attack by Germany. France had been invaded in 1914 and in 1870.’


10 marker on ‘Clemenceau achieved what he wanted in the Treaty of Versailles.’ How far do you agree with this statement? Explain your answer.
reasons for
-
I agree with this. Clemenceau wanted to make France safer from a German attack and he got some things that helped with this. He demanded the return of Alsace-Lorraine to France and this happened in the treaty. Germany was also made weaker by losing land that produced a lot of its iron ore and some of its coal. The reduction of its armed forces also made it weaker. All this meant that France was safer and this is what Clemenceau wanted.
reasons against
-
Clemenceau did not get a lot of what he wanted. He wanted France to be safe from a future German attack and so demanded that the USA and Britain give a guarantee that they would come to France’s aid if it was attacked by Germany. They did not agree to do this.’
10 marker on Who did Wilson find more difficult to deal with during the peace negotiations, Clemenceau or Lloyd George? Explain your answer.
reasons for Clemenceau
-
Clemenceau was more difficult to deal with for Wilson because he wanted such a harsh treaty and Wilson did not want this. Clemenceau was under pressure from the French people to achieve long-term security for France. Clemenceau wanted to punish and weaken Germany. He wanted very high reparations, Germany to lose the Rhineland, many of Germany’s colonies, and Alsace-Lorraine and the Saar Basin to be given to France. Most of these demands went against Wilson’s approach of a moderate treaty and self-determination. He wanted a settlement that would ensure peace in the future. This is why he found Clemenceau difficult to deal with.
reasons for Lloyd george
-
I think he found Lloyd George much more difficult to deal with. This was because Lloyd George kept changing his mind while Clemenceau knew what he wanted and stuck to it. At first, Lloyd George, under pressure from the British public, demanded a harsh treaty in which Germany should pay the full cost of the war. However, he then changed his mind and decided he wanted a more moderate settlement because he did not want Germany to become too weak. This made him difficult for Wilson to deal with.’
PPQs for Lloyd George
6 marker on why did Lloyd George favour a moderate peace settlement treaty with Germany
‘Lloyd George wanted a moderate peace settlement because he did not want Germany made too weak, especially economically. This was because Germany was an important trade partner of Britain’s and he wanted Germany strong enough to be able to trade with Britain. He wanted a Germany that could still buy plenty of British goods. This would be good for Britain and allow it to recover after the war.’
6 marker on why negotiations were difficult of Lloyd george
‘Negotiations were difficult for Lloyd George because he had to juggle different priorities. He did not want Germany to be punished so harshly that its economy could not recover. In the years before the war Germany was Britain’s biggest trading partner. He realised the economic wellbeing of Britain depended on an economically strong Europe. However, the British people were also keen to see that Germany was punished and Lloyd George’s political future rested on maintaining their support.’
10 marker on Lloyd George gained most of what he wanted in the Treaty of Versailles.’ How far do you agree with this statement?


reasons for:
‘Lloyd George did get most of what he wanted. He wanted a peace that would help Britain’s economy and he got that. Germany was not punished so harshly that it would not be able to recover. This was important because Britain did a lot of trade with Germany. Lloyd George also wanted a Germany that was strong enough to stand up to communism from the Soviet Union.’
reasons against:
Lloyd George did not get most of what he wanted. He did not want Germany to be punished too harshly but the anger that was created in Germany against the peace treaty showed that Lloyd George would be disappointed. He understood that this anger might lead to a bitter Germany that would want revenge in the future. He was particularly disappointed that German speakers had been put under French and Polish rule.’
10 marker on who was more satisfied with the Treaty of Versailles: Lloyd George or Wilson? Explain your
answer.
Reasons for Lloyd George:
‘Lloyd George felt that the Versailles Treaty punished Germany without destroying its economy or ability to contribute to
the future prosperity of Europe. This was good for British business and reassuring for those who feared the westward
spread of communism. Lloyd George returned from Paris in triumph and the House of Commons voted to approve the
treaty with an overwhelming majority.’
Reasons for Wilson:
‘Wilson was pleased that he had successfully persuaded his partners to accept that the Covenant of the League of
Nations should be included in all the peace treaties. This would help to make the new peace keeping organisation become
a reality. He was disappointed that the American Congress failed to approve the treaties and the League.’